Configuring a ROSA cluster to pull images from AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
Prerequisites
Note your ROSA cluster must be a classic STS cluster
Background
Quick Introduction by Ryan Niksch & Charlotte Fung on YouTube .
There are two options to use to authenticate wth Amazon ECR to pull images.
The traditional method is to create a pull secret for ecr.
Example:
oc create secret docker-registry ecr-pull-secret \
--docker-server=<registry id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com \
--docker-username=AWS --docker-password=$(aws ecr get-login-password) \
--namespace=hello-world
However Amazon ECR tokens expire every 12 hours which will mean you will need to re-authenticate every 12 hours either through scripting or do so manually.
A second, and preferred method, is to attach an ECR Policy to your cluster’s worker machine profiles which this guide will walk you through.
Attach ECR Policy Role
You can attach an ECR policy to your cluster giving the cluster permissions to pull images from your registries. ROSA worker machine instances comes with pre-defined IAM roles (ManagedOpenShift-Worker-Role) which we can add the ECR policy to.
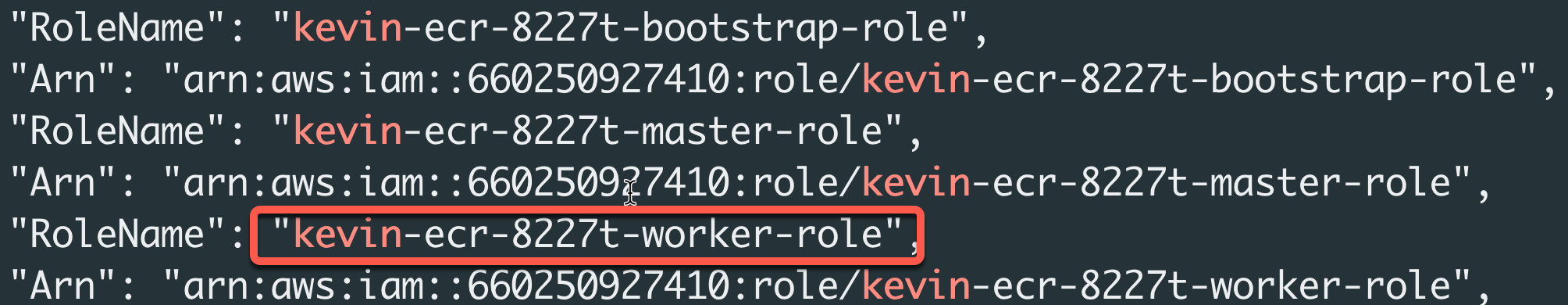
Note: If you used a different prefix for your Account Roles, you will need to change the following
aws iam attach-role-policycommand to suit.
Configure ECR with ROSA
ECR has several pre-defined policies that give permissions to interact with the service. In the case of ROSA, we will be pulling images from ECR and will only need to add the AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly policy.
Add the
AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnlypolicy to theManagedOpenShift-Worker-Rolefor STS clusters (or the<cluster name>-<identifier>-worker-rolefor non-STS clusters).STS Example:
aws iam attach-role-policy \ --role-name ManagedOpenShift-Worker-Role \ --policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly"Set ENV variables
Set our AWS Region and Registry name for creating a new ECR
REGION=us-east-2 REGISTRY=hello-ecrCreate a repository
aws ecr create-repository \ --repository-name $REGISTRY \ --image-scanning-configuration scanOnPush=true \ --region $REGIONSet Registry ID
REGISTRYID=`aws ecr describe-repositories --repository-name $REGISTRY | jq -r '.repositories[].registryId'`Log into ECR
podman login -u AWS -p $(aws ecr get-login-password --region $REGION) $REGISTRYID.dkr.ecr.$REGION.amazonaws.comPull an image
podman pull openshift/hello-openshiftTag the image for ecr
podman tag openshift/hello-openshift:latest $REGISTRYID.dkr.ecr.$REGION.amazonaws.com/hello-ecr:latestPush the image to ECR
podman push $REGISTRYID.dkr.ecr.$REGION.amazonaws.com/hello-ecr:latestCreate a new project
oc new-project hello-ecr
- Create a new app using the image on ECR
oc new-app --name hello-ecr --allow-missing-images \
--image $REGISTRYID.dkr.ecr.$REGION.amazonaws.com/hello-ecr:latest
- View a list of pods in the namespace you created:
oc get pods
Expected output:
If you see the hello-ecr pod running … congratulations! You can now pull images from your ECR repository.
Clean up
Simply delete the project you created to test pulling images:
oc delete project hello-ecrYou may also want to remove the
arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnlypolicy from the worker nodes if you do no want them to continue to have access to the ECR.
