Using Cluster Logging Forwarder in ARO with Azure Monitor
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
In Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) you can fairly easily set up cluster logging to an in-cluster Elasticsearch using the OpenShift Elasticsearch Operator and the Cluster Logging Operator, but what if you want to use the Azure native Log Analytics service?
There’s a number of ways to do this, for example installing agents onto the VMs (in this case, it would be a DaemonSet with hostvar mounts) but that isn’t ideal in a managed system like ARO.
Fluentd is the log collection and forwarding tool used by OpenShift, however it does not have native support for Azure Log Analytics. However Fluent-bit which supports many of the same protocols as Fluentd does have native support for Azure Log Analytics.
Armed with this knowledge we can create a fluent-bit service on the cluster to accept logs from fluentd and forward them to Azure Log Analytics.
Prepare your ARO cluster
Deploy an ARO cluster
Set some environment variables
export NAMESPACE=aro-clf-am export AZR_RESOURCE_LOCATION=eastus export AZR_RESOURCE_GROUP=openshift # this value must be unique export AZR_LOG_APP_NAME=$AZR_RESOURCE_GROUP-$AZR_RESOURCE_LOCATION
Set up ARO Monitor workspace
Add the Azure CLI log extensions
az extension add --name log-analyticsCreate resource group
If you plan to reuse the same group as your cluster skip this step
az group create -n $AZR_RESOURCE_GROUP -l $AZR_RESOURCE_LOCATIONCreate workspace
az monitor log-analytics workspace create \ -g $AZR_RESOURCE_GROUP -n $AZR_LOG_APP_NAME \ -l $AZR_RESOURCE_LOCATIONCreate a secret for your Azure workspace
WORKSPACE_ID=$(az monitor log-analytics workspace show \ -g $AZR_RESOURCE_GROUP -n $AZR_LOG_APP_NAME \ --query customerId -o tsv) SHARED_KEY=$(az monitor log-analytics workspace get-shared-keys \ -g $AZR_RESOURCE_GROUP -n $AZR_LOG_APP_NAME \ --query primarySharedKey -o tsv)
Configure OpenShift
Create a Project to run the log forwarding in
oc new-project $NAMESPACECreate namespaces for logging operators
kubectl create ns openshift-logging kubectl create ns openshift-operators-redhatAdd the MOBB chart repository to Helm
helm repo add mobb https://rh-mobb.github.io/helm-charts/Update your Helm repositories
helm repo updateDeploy the OpenShift Elasticsearch Operator and the Red Hat OpenShift Logging Operator
> Note: You can skip this if you already have them installed, or install them via the OpenShift Console.
helm upgrade -n $NAMESPACE clf-operators \ mobb/operatorhub --install \ --values https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rh-mobb/helm-charts/main/charts/aro-clf-am/files/operators.yamlConfigure cluster logging forwarder
helm upgrade -n $NAMESPACE clf \ mobb/aro-clf-am --install \ --set "azure.workspaceId=$WORKSPACE_ID" --set "azure.sharedKey=$SHARED_KEY"
Check for logs in Azure
Wait 5 to 15 minutes
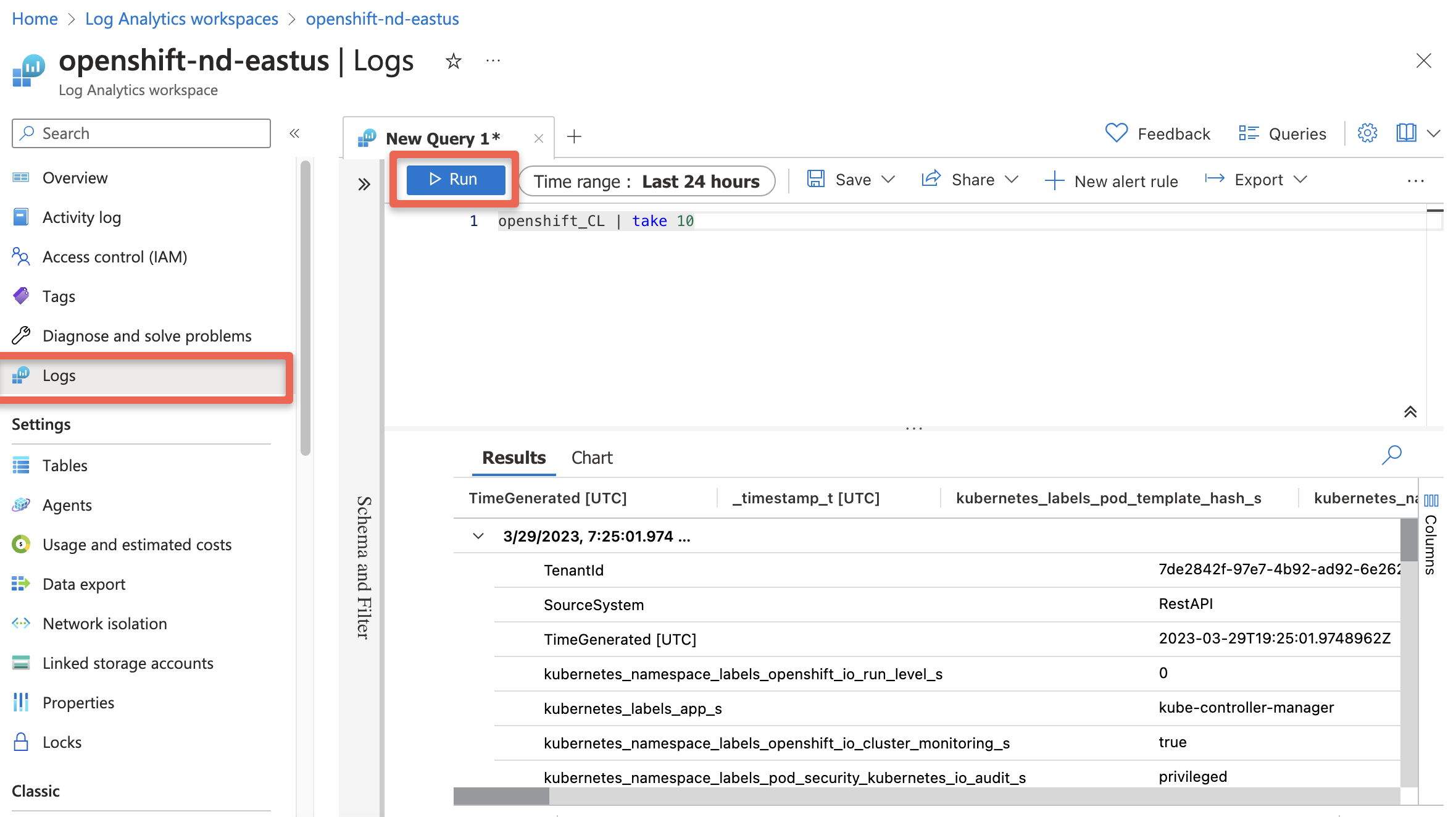
Query our new Workspace
az monitor log-analytics query -w $WORKSPACE_ID \ --analytics-query "openshift_CL | take 10" --output tsv
or
Log into Azure Azure Log Insights or you can login into portal and search for Log Analytics workspace
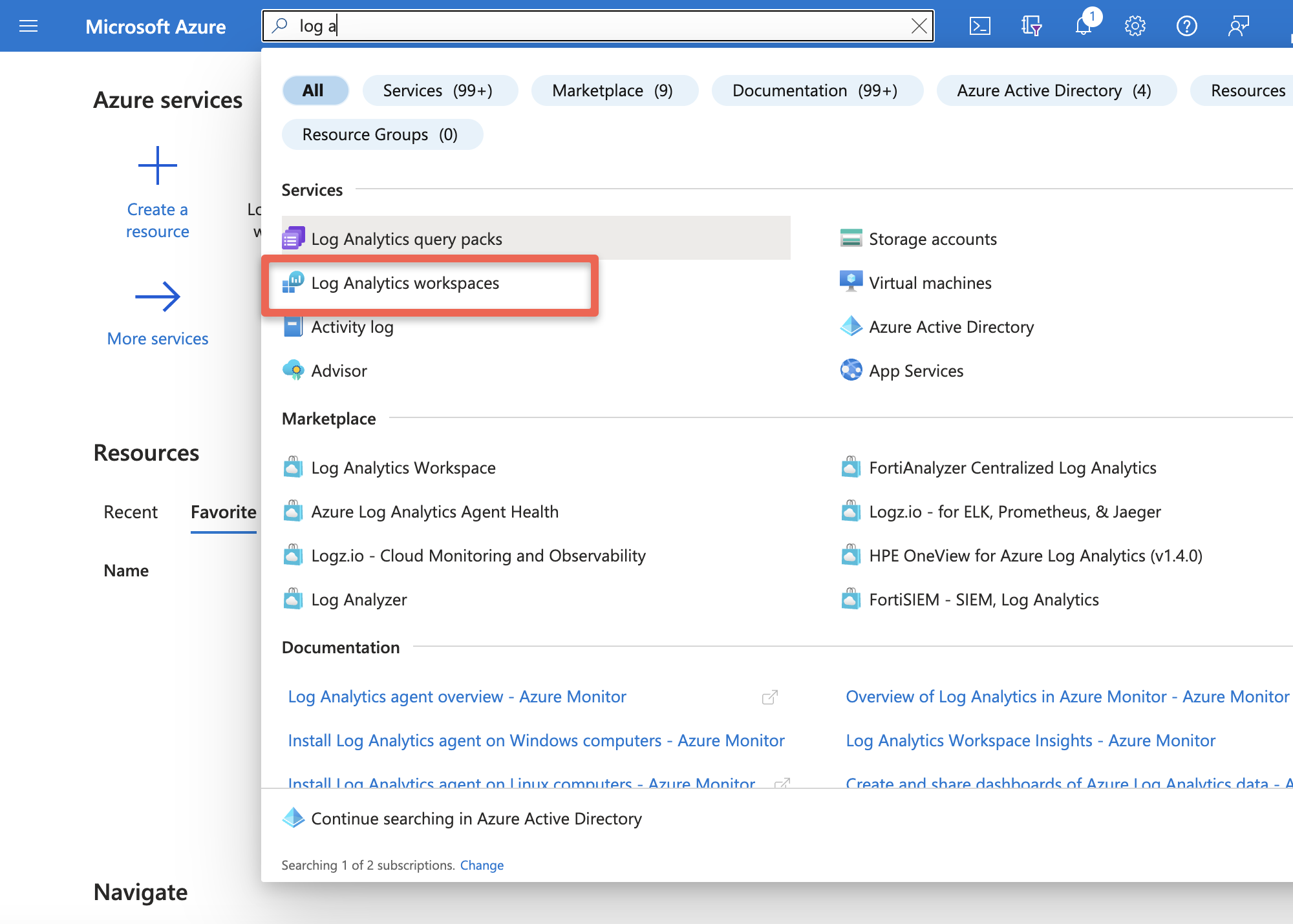
Select your workspace
Run the Query
openshift_CL | take 10